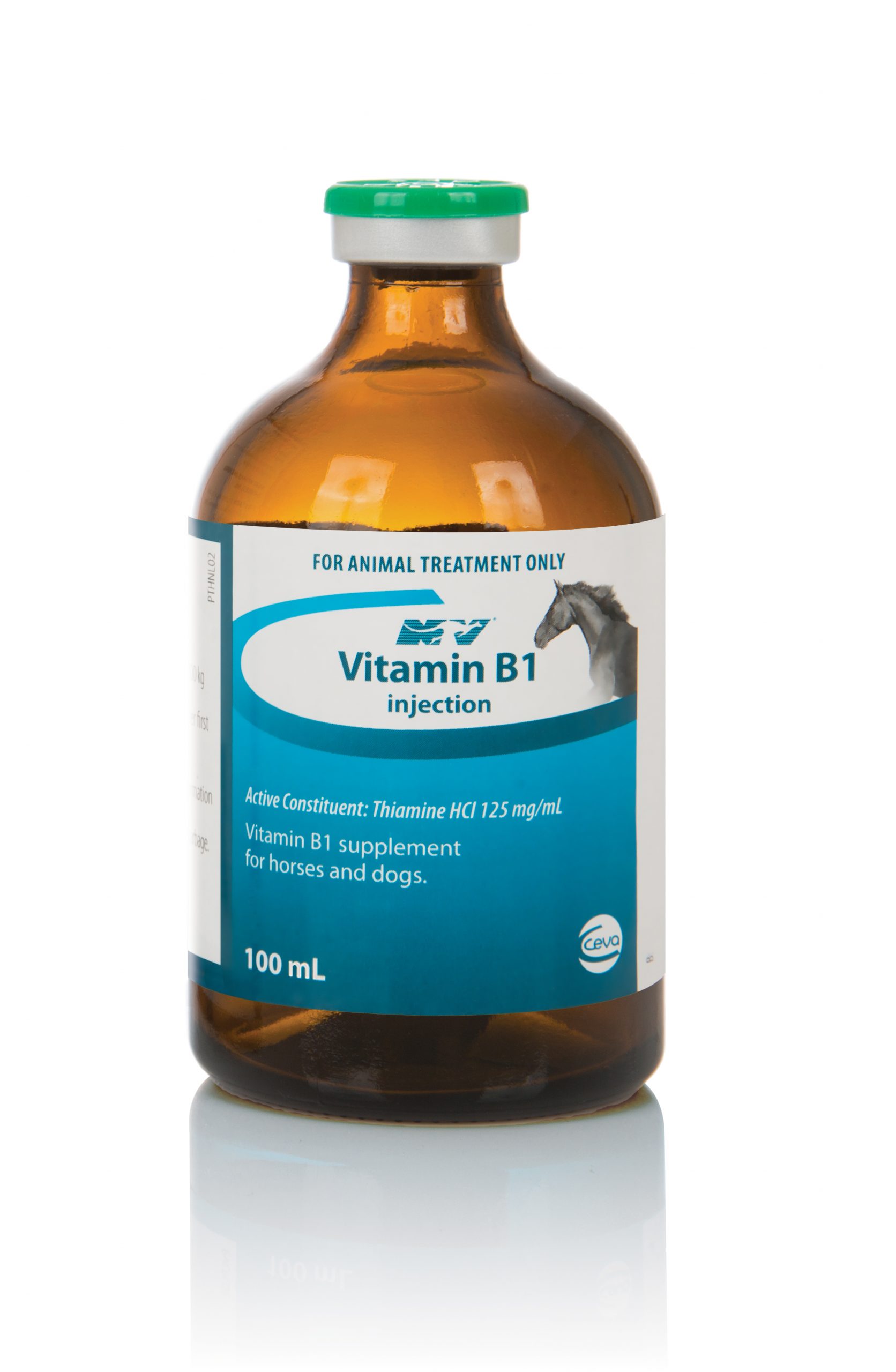
Description
Thiamine (Vitamin B1) plays an important role in the metabolism of carbohydrates and energy production for all cells. Thiamine is most important in the breakdown of pyruvic acid a waste product in hard working muscles along with lactic acid. In any situation where carbohydrates are the major energy source or when glucose is added to the diet thiamine requirement is increased significantly.
Thiamine is essential as part of the coenzyme which is involved in the breakdown of glucose for energy.
Thiamine in conjunction with Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) is essential in the metabolism of proteins and amino acids. Thiamine has effects on all tissues. The most sensitive are nerves stomach and heart.
Free Thiamine cannot be stored in the body and it is rapidly absorbed from the intestine or blood as well as from injection sites. Like all B Complex vitamins Thiamine is water soluble so it is rapidly absorbed and excreted from the body and requires regular supplementation especially in hard working animals when dietary input will probably not be sufficient.
Thiamine is found in both meat and cereal products. Small amounts are manufactured in the gut as long as horses are not under stress.
Thiamine in food is destroyed by cooking. Beef loses up to 75% of its Thiamine when cooked.
High doses of Thiamine are reported to help calm nervous or over excitable horses.
Clinical signs of Thiamine deficiency include fatigue muscle weakness loss of appetite and increased heart rate. (This may be an important factor in endurance horses fed high grain diets).
Many of these signs can be traced back to increased tissue levels of lactic and pyruvic acids. Nerve cells are particularly dependant on carbohydrate metabolismand normal nerve function is greatly effected by increased levels of these acids during hard work.
Indications:
None
Dosage and Adminstrations:
Give 5 – 10mL by intramuscular injection regularly twice weekly or as advised by a veterinary surgeon.